sort
Sort array elements
Description
B = sort(A)A in ascending order.
If
Ais a vector, thensort(A)sorts the vector elements.If
Ais a matrix, thensort(A)treats the columns ofAas vectors and sorts each column.If
Ais a multidimensional array, thensort(A)operates along the first array dimension whose size does not equal 1, treating the elements as vectors.
B = sort(___,Name,Value)sort(A,'ComparisonMethod','abs') sorts
the elements of A by magnitude.
Examples
Sort Vector in Ascending Order
Create a row vector and sort its elements in ascending order.
A = [9 0 -7 5 3 8 -10 4 2]; B = sort(A)
B = 1×9
-10 -7 0 2 3 4 5 8 9
Sort Matrix Rows in Ascending Order
Create a matrix and sort each of its rows in ascending order.
A = [3 6 5; 7 -2 4; 1 0 -9]
A = 3×3
3 6 5
7 -2 4
1 0 -9
B = sort(A,2)
B = 3×3
3 5 6
-2 4 7
-9 0 1
Sort Matrix Columns in Descending Order
Create a matrix and sort its columns in descending order.
A = [10 -12 4 8; 6 -9 8 0; 2 3 11 -2; 1 1 9 3]
A = 4×4
10 -12 4 8
6 -9 8 0
2 3 11 -2
1 1 9 3
B = sort(A,'descend')B = 4×4
10 3 11 8
6 1 9 3
2 -9 8 0
1 -12 4 -2
Sort String Array
Starting in R2017a, you can create string arrays using double quotes, and sort them using the sort function. Sort strings in each column of a string array according to Unicode® dictionary order.
A = ["Santos","Burns"; ... "Jones","Morita"; ... "Petrov","Adams"]; B = sort(A)
B = 3x2 string
"Jones" "Adams"
"Petrov" "Burns"
"Santos" "Morita"
Sort the strings in each row.
B = sort(A,2)
B = 3x2 string
"Burns" "Santos"
"Jones" "Morita"
"Adams" "Petrov"
Sort and Index datetime Array
Create an array of datetime values and sort them in ascending order, that is, from the earliest to the latest calendar date.
ds = {'2012-12-22';'2063-04-05';'1992-01-12'};
A = datetime(ds,'Format','yyyy-MM-dd')A = 3x1 datetime
2012-12-22
2063-04-05
1992-01-12
[B,I] = sort(A)
B = 3x1 datetime
1992-01-12
2012-12-22
2063-04-05
I = 3×1
3
1
2
B lists the sorted dates and I contains the corresponding indices of A.
Access the sorted elements from the original array directly by using the index array I.
A(I)
ans = 3x1 datetime
1992-01-12
2012-12-22
2063-04-05
Sort Vectors in Same Order
Create two row vectors that contain related data in the corresponding elements.
X = [3 6 4 2 1 5]; Y = ["yellow" "purple" "green" "orange" "red" "blue"];
First sort the vector X, then sort the vector Y in the same order as X.
[Xsorted,I] = sort(X)
Xsorted = 1×6
1 2 3 4 5 6
I = 1×6
5 4 1 3 6 2
Ysorted = Y(I)
Ysorted = 1x6 string
"red" "orange" "yellow" "green" "blue" "purple"
Sort 3-D Array
Create a 2-by-2-by-2 array and sort its elements in ascending order along the third dimension.
A(:,:,1) = [2 3; 1 6]; A(:,:,2) = [-1 9; 0 12]; A
A =
A(:,:,1) =
2 3
1 6
A(:,:,2) =
-1 9
0 12
B = sort(A,3)
B =
B(:,:,1) =
-1 3
0 6
B(:,:,2) =
2 9
1 12
Use A(:), the column representation of A, to sort all of the elements of A.
B = sort(A(:))
B = 8×1
-1
0
1
2
3
6
9
12
Complex Vector
Sort the elements of a complex vector by their real parts. By default, the sort function sorts complex values by their magnitude, and breaks ties using phase angles. Specify the value of 'ComparisonMethod' as 'real' to instead sort complex values by their real parts. For elements with equal real parts, sort breaks the tie based on their imaginary parts.
A = [1+2i 3+1i 1i 0 -1i]; B = sort(A,'ComparisonMethod','real')
B = 1×5 complex
0.0000 - 1.0000i 0.0000 + 0.0000i 0.0000 + 1.0000i 1.0000 + 2.0000i 3.0000 + 1.0000i
Input Arguments
A — Input array
vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Input array, specified as a vector, matrix, or multidimensional array.
If
Ais a scalar, thensort(A)returnsA.If
Ais complex, then by default,sortsorts the elements by magnitude. If more than one element has equal magnitude, then the elements are sorted by phase angle on the interval (−π, π].If
Ais a cell array of character vectors or a string array, thensort(A)sorts the elements according to the code order for the UTF-16 character encoding scheme. The sort is case-sensitive. For more information on sorting character and string arrays, see Sort Order for Character and String Arrays.If
Ais a string array, thensortreorders the elements of the array, but does not reorder characters within the strings.If
Ais a categorical array, then the sorting order is based on the category order returned bycategories(A).
Data Types: double | single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | cell | categorical | datetime | duration
Complex Number Support: Yes
dim — Dimension to operate along
positive integer scalar
Dimension to operate along, specified as a positive integer scalar. If no value is specified, then the default is the first array dimension whose size does not equal 1.
Consider a matrix
A.sort(A,1)sorts the elements in the columns ofA.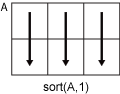
sort(A,2)sorts the elements in the rows ofA.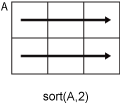
sort returns A if dim is
greater than ndims(A). dim is
not supported when A is a cell array, that is, sort only
operates along the first array dimension whose size does not equal
1.
Data Types: double | single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
direction — Sorting direction
'ascend' (default) | 'descend'
Sorting direction, specified as 'ascend' or 'descend'. direction is
not supported when A is a cell array, that is, sort only
sorts in ascending order.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: sort(A,'MissingPlacement','last')
MissingPlacement — Placement of missing values
'auto' (default) | 'first' | 'last'
Placement of missing values (NaN, NaT, <undefined>,
and missing) specified as the comma-separated pair
consisting of 'MissingPlacement' and one of the
following:
'auto'— Missing elements are placed last for ascending order and first for descending order.'first'— Missing elements are placed first.'last'— Missing elements are placed last.
ComparisonMethod — Element comparison method
'auto' (default) | 'real' | 'abs'
Element comparison method, specified as the comma-separated
pair consisting of 'ComparisonMethod' and one of
the following:
'auto'— SortAbyreal(A)whenAis real, and sort byabs(A)whenAis complex.'real'— SortAbyreal(A)whenAis real or complex. IfAhas elements with equal real parts, then useimag(A)to break ties.'abs'— SortAbyabs(A)whenAis real or complex. IfAhas elements with equal magnitude, then useangle(A)in the interval (-π,π] to break ties.
Output Arguments
B — Sorted array
vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Sorted array, returned as a vector, matrix, or multidimensional array. B is
the same size and type as A.
Data Types: double | single | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | cell | categorical | datetime | duration
I — Sort index
vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Sort index, returned as a vector, matrix, or multidimensional
array. I is the same size as A.
The index vectors are oriented along the same dimension that sort operates
on. For example, if A is a 2-by-3 matrix, then [B,I]
= sort(A,2) sorts the elements in each row of A.
The output I is a collection of 1-by-3 row index
vectors describing the rearrangement of each row of A.
The sort function uses a stable sorting algorithm. So,
when the input contains repeated values, the sort index preserves the
original order from the input, regardless of sorting direction. For example,
if A = [1 2 1 2], then [Ba,Ia] =
sort(A,'ascend') returns the sort index Ia = [1 3 2
4] and [Bd,Id] = sort(A,'descend') returns
the sort index Id = [2 4 1 3].
More About
Sort Order for Character and String Arrays
MATLAB® stores characters as Unicode® using the UTF-16 character encoding scheme. Character and string arrays are sorted according to the UTF-16 code point order. For the characters that are also the ASCII characters, this order means that uppercase letters come before lowercase letters. Digits and some punctuation also come before letters.
Tips
The
sortrowsfunction provides additional flexibility for subsorting over multiple columns of matrix or table inputs.The
sortfunction and the relational operators use different orderings for complex numbers. For more information, see Relational Operations.
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
This function supports tall arrays with the limitations:
You must specify the dimension to sort, as in
sort(X,dim).Sorting the tall dimension, as in
sort(X,1), is only supported for column vectors.
For more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
Usage notes and limitations:
If
Ais complex with all zero imaginary parts, then MATLAB might convertAtoreal(A)before callingsort(A). In this case, MATLAB sortsAbyreal(A), but the generated code sortsAbyabs(A). To make the generated code match MATLAB, usesort(real(A))orsort(A,'ComparisonMethod','real'). See Code Generation for Complex Data with Zero-Valued Imaginary Parts (MATLAB Coder).If you supply
dim, then it must be constant.Variable-sizing support must be enabled when input cell array is heterogeneous.
For limitations related to variable-size inputs, see Variable-Sizing Restrictions for Code Generation of Toolbox Functions (MATLAB Coder).
GPU Code Generation
Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
Refer to the usage notes and limitations in the C/C++ Code Generation section. Same limitations apply to the GPU Code Generation.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Usage notes and limitations:
Table, timetable, and datetime inputs are not supported.
For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced before R2006a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)